|
|
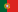
L9 SAVM: Sociedade Agrícola Vargas Madeira Lda (PT) |
||||
|
|
|||||
|
FUNCTIONS APPLIED TO THE LAND |
|||||
|
ECONOMIC |
|||||
|
Aromatics [1] |
Managing and valorizing local aromatic plants, mainly Lavandula viridis and Lavandula stoechas, for the self-extraction of essential oils. |
||||
|
Fruits & nuts water demanding [7, 15] |
Former abandoned orchard was rehabilitated. Orange, prunes, apples, lemons, pears, peaches, apricots, kaki, walnut production for self-use and sails in local market. |
||||
|
Fodder as buffer zone [9] |
Some plants are used for fodder, trees are pruned for firewood, main economic return is avoided costs. |
||||
|
Fodder [9] |
This is a large fodder bank. When the bank has grown enough to sustain the grazing, cattle can go in. Main economic return is avoided costs. |
||||
|
Timber + firewood + nuts [19, 15] |
These 6 clusters are installed inside an old reforestation project. Plants were selected to improve biodiversity, for timber production through pruning and nut production. Furthermore, test will be carried out for grafting Pistacia vera on Pistacia terebintus that is more resistant to drought. |
||||
|
Pasture improvement + livestock [4, 20]
|
Holistic planned grazing is set to optimize the use of grass by sheeps reducing the grazing pressure, increasing grass productivity, reducing the need for external feed and relative costs, increasing ecosystem quality. |
||||
|
ECOSERVICES |
|||||
|
Campground/B&B [25] |
A small family house will be transformed in a B&B and products made in the rest of the properties as well as ecoservices proposed to B&B clients. | ||||
|
Hiking trails [27] |
Connecting with existing routes. No new routes required. | ||||
|
Photo hunting [29] |
There is a feeding place for black vultures (old Life program). | ||||
|
Test Area [32] |
Testing various species that might work in the future in a Montado system, as well as old varieties of fruits and nuts. |
||||
|
Study and guided tours [35] |
When hiking trails have been established, guided tours will be planned. | ||||
|
ENVIRONMENTAL |
|||||
|
Fruits & nuts less water demanding [7, 15] |
Former abandoned orchard was rehabilitated. Plants such as mulberry, fig, carob, arbutus, and olive wild were selected to attract birds and mammals and promote biodiversity. | ||||
|
Fodder + nuts + berries as a cluster of biodiversity [7, 15, 18] |
Biodiversity islands created as hotspots act as core of accretion. | ||||
|
Erosion control [37] |
Stone flood walls restored, no tillage, holistic planned grazing. | ||||
|
Insect and bird shelter [40] |
Bird and bat houses, as well as insect hotels installed to increase biodiversity of beneficial organisms like pollinators and natural enemies of pest. |
||||
|
Reforestation/Afforestation [41] |
Area of intervention to increase tree cover density by planting native oaks and also carob tree, which are climate resilient and provide feed for animals. |
||||
|
Rivers & Open water [42]
|
Lake protection. Planting aquatic plants for filtration. To avoid erosion around ponds due to the livestock trampling, fences were installed around ponds. Solar pumping system mounted on a raft to bring the water up. |
||||
|
Rivers & Open water [42] |
Streambed protection. Protection of water reservoirs with buffer plant ones, barrier for animals, and water extraction with solar panels to avoid animal disturbance and soil erosion around the water basin. |
||||
|
Landscape Restoration [45] |
Re-building new flood walls where old walls once were set. In the steepest areas this allows to control water flow and soil erosion. |
||||
|
Biodiversity promoting plants [46] |
Increase plant biodiversity in protected areas to support insects, birds and mammals biodiversity. |
||||
|
SOCIAL |
|||||
|
Create employment [47] |
Optimization of working hours and organization. | ||||
|
Provide social service [49] |
Working with schools. | ||||
| MEASURES APPLIED TO THE LAND | |||||
| N. | Name | Comments | |||
| 1 | Seed collecting & native species | Oak acorns used for reforestation. | |||
| 3 | Existing vegetation protection |
Landowner uses shrub shredder but leave plants roots and soil intact. Trees are protected from tillage that might damage the roots. |
|||
| 10 | Soil ripping |
Done only when necessary in conjunction with ridge and furrows. |
|||
| 11 | Conservation Tillage |
Everywhere no tillage for this property. |
|||
| 12 | Ridge and furrows |
Swales are made with small plows, to help retain water. This technique is preferred to half-moons due to the complexity to implement this technique on the stony soil over slopes that makes it too costly. |
|||
| 14 | Organic fertilizer |
Collection and application of sheep manure. Cows are always outdoor. |
|||
| 23 | Planting in mixes |
Used to implement biodiversity at all levels. |
|||
| 26 | Plant support Water aids study |
The cocoons method was tested but did not produce optimal results on this kind of environment. |
|||
| 27 | Watering/Drip irrigation |
Everywhere drip irrigation, based on water coming from dams and cisterns and used when plants get water stressed. |
|||
| 29 | Plant assist |
Seedling protectors. |
|||
| 31 | Grafting trees | Selection of natural occurring wild rootstocks for grafting afterwards. For example, Pistacia vera will be grafted on Pistacia terebintus that is more resistant to drought. | |||
| 32 | Diseased trees |
Re-planting is foreseen using local seeds. |
|||
| 33 | Weed control |
Only cutting or grazing, no chemicals and weeding. |
|||
| 35 | Prunings |
It is done using appropriate schemes that do no stress trees. |
|||
| 37 | Livestock Grazing |
A holistic planned grazing is being applied. |
|||
| 44 | Firewood 10% rule |
10% of the dead wood is always left on the site. |
|||
| 52 | Root protection |
No machines are used any more to plough and till. |
|||
|
Numbers of functions and measures correspond to the list reported in the DAM methodology, defining the operative DAM plan http://www.desert-adapt.it/index.php/en/case-studies/dam-methodology |
|||||
| FIELD IMPLEMENTATION OF THE DAM PLAN | |||||
|
Pasture improvement and holistic planned grazing [Economic functions: pasture improvement 20 and livestock 4] The landowner of Sociedade Agrícola Vargas Madeira Lda, Joao Madeira, adopted the Holistic Managment Planning as part of the Desertification Adaptation Model plan for his farm. The farm breeds sheep and cows and has been experiencing over time a critical decrease of grass productivity, requiring external interventions like intercropping with leguminous and fertilization, with, however, minor results. Another consequence of the low grass productivity and overgrazing is a higher degree of compaction in time and bare soil exposed to erosion processes during the driest months, once the animals have grazed the available grass biomass (Pict.1-2). Pictures from 3 and 4 show the shallow roots of grass in the site before the introduction of the alternative management plan. The holistic planned grazing is based on time-controlled grazing systems. Land is divided into grazing paddocks demarcated by fences or natural barriers, in order to be in control of the livestock movements. By having more animals grazing for a short time, paddocks turn is longer and this allow the grass to fully recover the above ground biomass, which photosynthetic activity can then support the creation of stronger and deeper roots which in turn can make better use of resources (water and minerals) and feedback higher productivity rates. Pictures from 5 to 9 show the sequential steps of grass growth from the peak in the first season before summer grazing to the next one. Both amount and quality of grass are improved, and after the summer grazing (Pict. 7) the soil is not bare any more compared to the situation before the management change but already shows green vegetation. It is also possible to appreciate the dense biomass of the dry grass in the first (Pict. 5-6) and second (Pict. 9) summer after the introduction of rotation management. |
|||||
|
|||||
|
Water collection for livestock and streambed protection [Environmental function: open water & streambed protection 42] A buffer zone composed of plants was created along the river (Pict.1-3) to protect water. The buffer zone has many functions including protection from erosion and hence siltation and capture of nutrients. Planted seedling, such as Phillyrea angustifolia and Rhamnus alaternus were protected with both plastic tube shelter and cactus protectors (metallic cages). Additionally, to avoid erosion around existing ponds due to the livestock trampling, the ponds were fenced and the water was provided to animals by introducing a solar pumping system mounted on a raft to bring the water up to the level of animal usage (Pict. 4-7). |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Fodder as buffer zone [Economic function: fodder 9] The soil of this area is characterized by poor drainage and a ridge-furrow planting design was adopted (Pict. 1-3). Two rows, one at each side of the streambed were planted (pict. 4) with plants used for both fodder (carob) and firewood. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Biodiversity cluster as productive areas for erosion control [Economic functions: nuts 15 – timber 19; Environmental function: erosion control 37] Six biodiversity clusters are being installed in areas at high erosion risk in the northern site (Pict. 1). Such areas were in some case terraced (Pict. 2) before planting (Pict. 3) to reduce surface runoff and soil loss. All seedlings were protected with plastic tube shelter and areas were fenced to reduce animal disturbance (Pict. 4). Furthermore, to support plant survival in driest periods, an emergency drip irrigation system was installed (Pict. 5-6). On the whole, these clusters (Pict. 7-9) act as biodiversity hotspots, productive areas (timber and nut) and erosion regulating measure. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Reforestation/Afforestation [Environmental function: 41] In the northern site the area devoted to afforestation (Pict. 1) was managed to increase tree cover density. A ridge-furrow planting was conducted to help to retain water and hence reduce surface soil loss. Farrow planting line were made with small plows (Pict. 2-5). Native oaks and carob seedlings were protected with plastic tube shelters against wild animals (Pict. 6-7) and an emergency drip irrigation system was installed for the driest period. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Biodiversity islands within pasture landscape [Economic functions: fruits 7 – nuts 15 – berries 18] Ten biodiversity clusters were created in the flat southern pasture site to stimulate biodiversity of woody species and related animal interactions. The concept of planting as an island rather than planting scattering trees is meant to increase the survival rate of tree by allowing for fencing of the area to avoid animal grazing and by positive interactions among planted trees, to reach same objective with lower costs, to act as an attraction center for birds and small mammals that can also help to diffuse seeds around. To date, the cluster areas have been marked off (Pict. 1-3) and soil has been superficially plowed (Pict. 4-6) to subsequently accommodate trees in middle rows and shrubs on sides. The areas will be fenced before planting. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Cocoon testing [Adaptation Measure: plant support & water aid 26] In the farm the plant water aid “cocoons” (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sll6IO65vPg) were tested, as a mean to improve the seedling survival rates in the first years after planting under harsh environmental conditions (Pict. 1). A shallow soil and a high rock fragments amount at the surface made cocoon installation difficult (Pict. 2-6). For the same reasons cocoons did not produce optimal results, many damages were done to the biodegradable container by sharp stones (Pict. 7), and sometimes cocoons collapsed (Pict. 8). The results indicated that this technique might not be ideal in this kind of soil and other nature based solution to increase soil water retention and reduce evapotranspiration can be applied (see the DAM methodology dedicated page, http://www.desert-adapt.it/index.php/en/casi-studio/dam-methodology/2-non-categorizzato/100-3-defining-the-operative-dam-plan). |
|||||
|
|
|||||