|
|
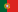
L5 Hoyos: Ayuntamiento de Hoyos (SP) |
||||
|
|
|||||
|
FUNCTIONS APPLIED TO THE LAND |
|||||
|
ECONOMIC |
|||||
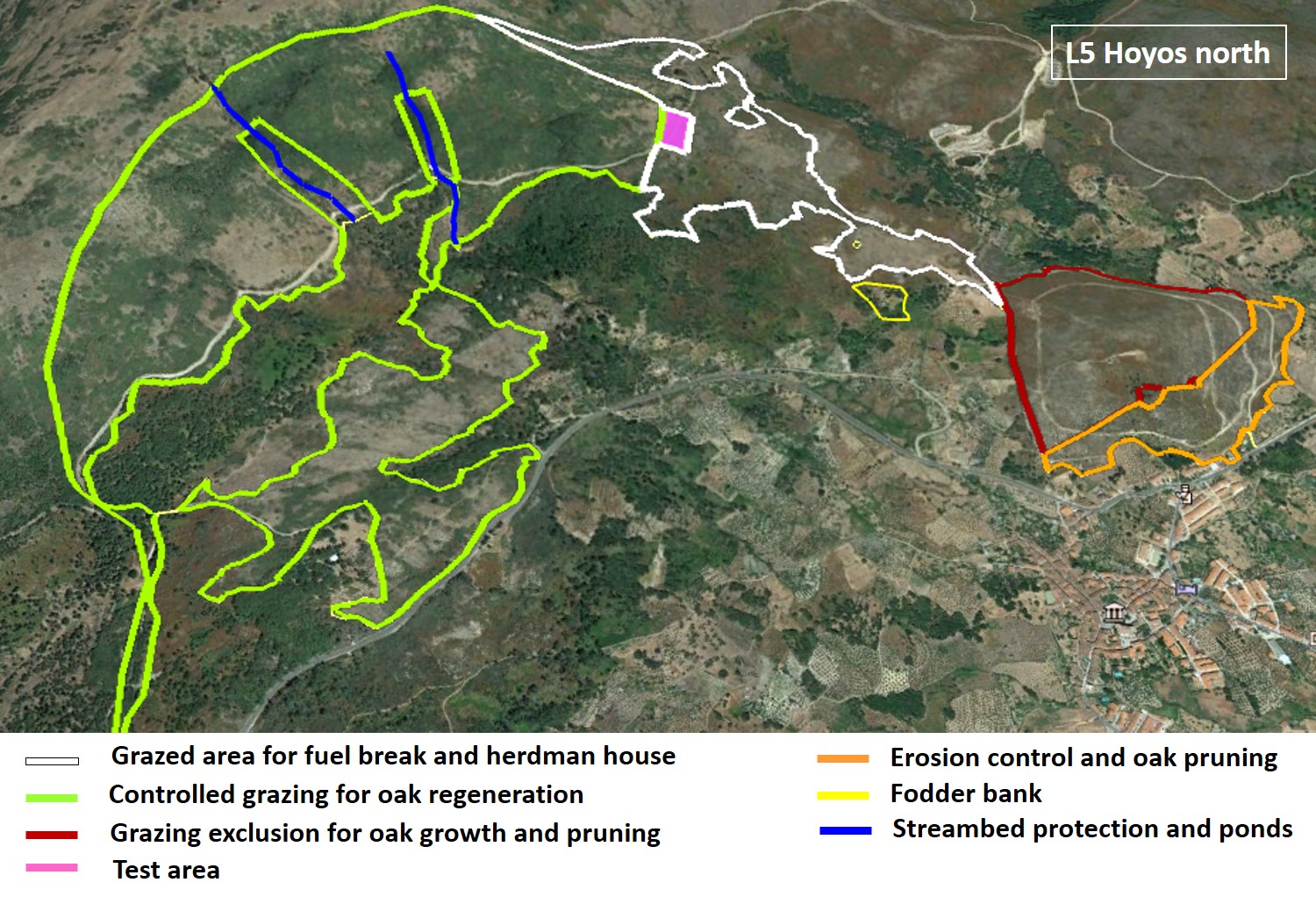
| Aromatics
[1] |
Small plots planted with Lavandula luisieri with minimum soil alteration. Main goal is extraction of essential oils but also very useful for attracting pollinators. |
||||
|
Sheep grazing under olive trees [4] |
Small private area under organic olive management with sheep grazing to prevent fire and shrub encroaching. | ||||
|
Sheep grazing in chestnut area [4] |
Two areas were sheep grazing is used to avoid shrub encroaching around old and new chestnut trees. |
||||
|
Grazed area for fuel break and herdsman house [4]
|
This large area is being continuously grazed by goats driven by a herder. The goat house has been improved and two water ponds have been built to ensure that goats use intensively this area and also attract wildlife in summer. | ||||
|
Pasture improvement [20] |
Small private area grazed by sheep and improved through manure and phospates. | ||||
|
Chestnut for fruit [15] |
A private area owned by local Association and targeting chestnut fruit production in newly planted trees. Owner aims chestnut fruit processing for flour and marron glacé. | ||||
|
Chestnut for fruit and for timber [13, 19] |
A private area owned by local Association and targeting small-scale timber harvesting from chestnut and chestnut fruit production in newly planted trees. | ||||
|
Recover of burnt cork oak [13, 19] |
A cork oak open forest that was affected by fire in 2015 in which partial shrub removal stimulate oak growth and cork production while reducing fire risk. | ||||
|
Fodder bank [9] |
A small fenced area planted with palatable tree species for goats in summer. | ||||
|
ECOSERVICES |
|||||
|
Test area [32] |
This area has been planted twice with a mixture of aromatic plant species in stone terraces that has been also repaired. This plot will be the basis for plant harvesting and processing by a local company selling organic cosmetics. |
||||
|
Hiking trails [27, 28, 35] |
A long path were shrubs have been removed to allow hiking through the main project areas. | ||||
|
ENVIRONMENTAL |
|||||
|
Erosion control and oak pruning [37, 15] |
In this area a slope with high soil loss after 2015 fire has been stabilized with stone walls (made by regional agency). The project has regulated goat access and facilitated shrub expansion and tree growth. | ||||
|
Streambed protection and ponds [42] |
Two seasonal streams planted with riparian trees and two ponds used by goats and wildlife. | ||||
|
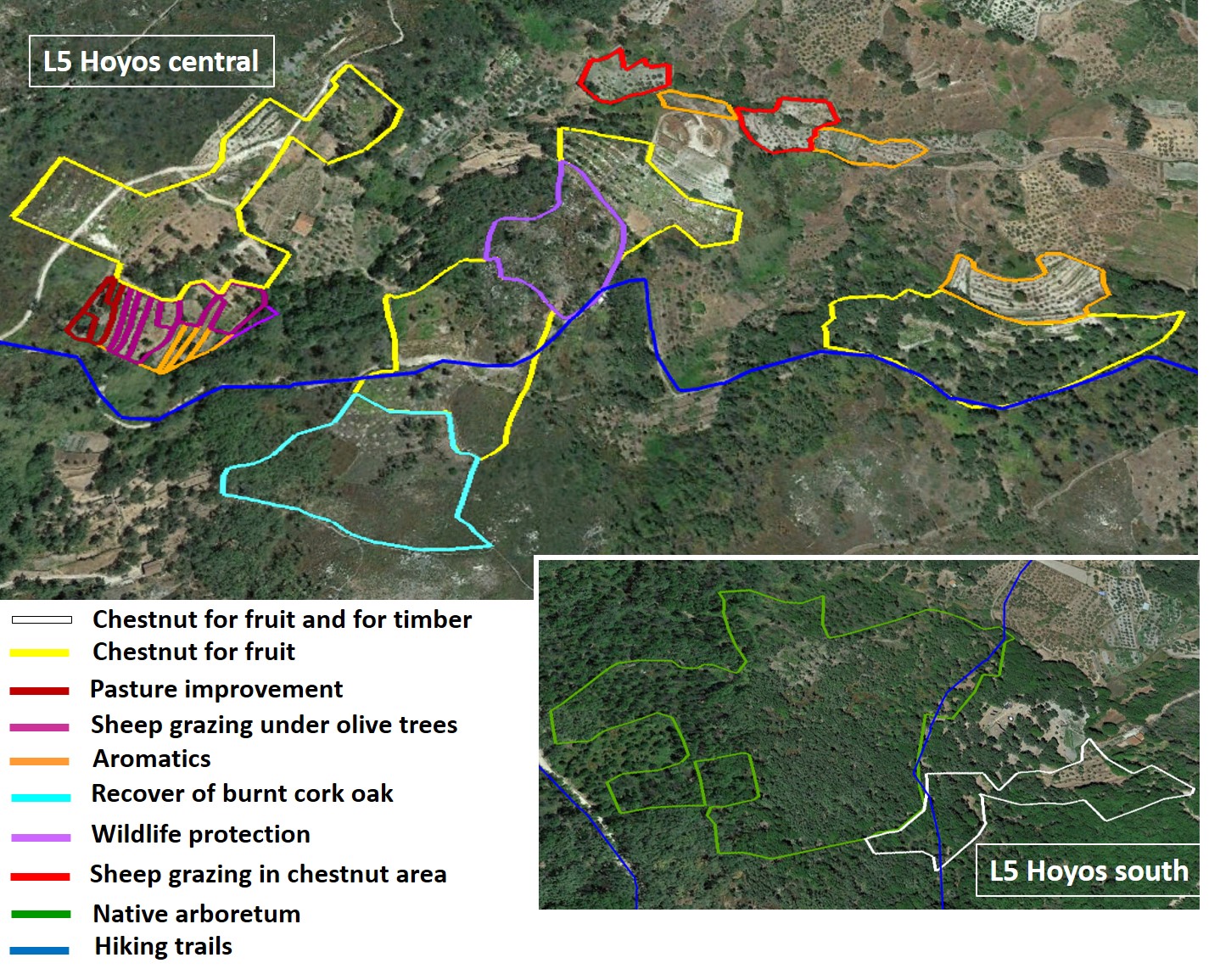
Native arboretum [41] |
Fenced botanical garden made up with native rare species of trees. The area also hosts traditional stone buildings and picnic facilities. |
||||
|
Controlled grazing for oak regeneration [41] |
A large area that burned in 2015 and is regenerating without planting just by regulating goat and cattle grazing in oak forest. | ||||
|
Grazing exclusion for oak growth and pruning [41, 15, 13] |
An area that has been fenced to reduce goat impact and to improve oak regeneration by pruning the trees and removing shrubs underneath. | ||||
|
Insect shelter [40] |
Stone hills for rabbits, maters, foxes etc. bird houses etc. | ||||
|
Wildlife protection [39] |
Two areas were plant species diversity has been increased by planting and wildlife has been supported with next boxes. | ||||
|
Landscape restoration [45] |
Repair some stone walls and old paths. Specifically, local Association wishes to restore a medieval path leading to the educational forest. | ||||
|
Biodiversity promoting planting [46] |
Increase plant biodiversity to support insects, birds and mammals biodiversity. | ||||
|
SOCIAL |
|||||
|
Create employment [47] |
Very Important part of the project which has hired local people both in external services and in cofinancing work. | ||||
|
Provide social services [49] |
Benches and picnic areas, and info panels in some places. | ||||
| MEASURES APPLIED TO THE LAND | |||||
| N. | Name | Comments | |||
| 1 | Seed collecting |
Almost all our plants como from local seed sources and nurseries have to use them also. |
|||
| 3 | Existing vegetation |
Vegetation has been removed only in small plots for aromatics or around trees in chestnut plots. |
|||
| 7 | Swales | ||||
| 9 | Half-moons | Used in slopes to retain water. | |||
| 10 | Soil ripping | ||||
| 11 | Conservation Tillage | Used only in small aromatic plots | |||
| 13 | Capture & Store Water | ||||
| 14 | Organic fertilizer |
Only organic fertilizer was used in the initial planting of fruit trees. |
|||
| 19 | Nurse shrubs | ||||
| 21 | Plant hole digging | ||||
| 22 | Interplanting | ||||
| 23 | Planting in mixes | ||||
| 24 | Regular planting | ||||
| 27 | Watering/Drip irrigation |
For chesnut, a tank delivering water on individual trees was used. |
|||
| 28 | Plant protectors |
Tubex protectors are used. |
|||
| 29 | Plant assist |
Stones, chips and plant remains used according to availability. |
|||
| 30 | Fencing installation | ||||
| 31 | Grafting trees | ||||
| 32 | Diseased trees | ||||
| 33 | Weed control |
Controlled by sheep. |
|||
| 34 | IPM Plague control | ||||
| 37 | Livestock Grazing |
No formalplan but regulation to avoid damage of regeneration and plantations. |
|||
| 44 | Firewood 10% rule |
Dead wood left intact in all plots. |
|||
| 45 | Natural Regeneration | ||||
| 51 | Planting material | ||||
|
Numbers of functions and measures correspond to the list reported in the DAM methodology, defining the operative DAM plan http://www.desert-adapt.it/index.php/en/case-studies/dam-methodology |
|||||
| FIELD IMPLEMENTATION OF THE DAM PLAN | |||||
|
Improving nut production from chestnut [Economic function: nuts 15; Adaptation Measures: plant protectors 28 - plant assist 29] Hoyos has planted several species, to increase the density of production of marketable goods like those derived from chestnut (Pict. 1-3) and also native local species increase biodiversity and cover density. Plant support measures have been used during seedling planting; mulching with local chipped wood (Pict. 4-6) seedlings plant protector and shelters (Pict. 7-11). |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Productive firewall [Economic functions: Aromatics 1 - Livestock 4 - Fodder 9 - Fruits 7 - Natural fibers 13 - Nuts 15 - Timber 19 - Pasture improvement 20] Municipality of Hoyos is also partner of MOSAICO project that aim at creating a mosaic landscape with less fire risk due to the adoption of a participatory fire prevention strategy based on agricultural, livestock and forestry activities (https://www.mosaicoextremadura.es/en/home-en/). These land portions represent productive firebreaks. Desert-adapt is networking with MOSAICO project on this topic. In Hoyos, the permanent production of aromatic plants (Pict. 1-2) will contribute to create local jobs thanks to the extraction of oils and resins used medicinally and cosmetically, as well as, to improve many ecosystem services such as the pollination and erosion control. Desert Adapt further promotes to restore terraces on slope to control erosion and preserve a precious cultural heritage that is disappearing (Pict. 3). The agro-silvo-pastoral uses act as productive and persistent firebreaks. Water sources (Pict. 4-6) as well as refuges (Pict. 7) for goats were repaired and grazing strategically planned to reduce the amount of vegetation that acts as fuel (Pict. 8-9). To sustain goat in summer a small area was planted with palatable tree species (Tagasaste, Pict. 10). Other project plots are devoted to nuts planting (Pict. 11-12) for fruits as well as timber (Pict. 13-14) and natural fibers (Pict. 15) production. |
|||||
|
Erosion control and natural regeneration [Environmental function: erosion control 37] In the map of Hoyos north the orange color indicates an area burned in 2015 where strong erosion is occurring. To reduce soil loss rate, the slope has been stabilized by the creation of stone walls (Pict. 1) and the goat grazing has been used to facilitated natural regeneration of shrub and tree (Pict. 2-3). |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Functions to improve ecoservices [test area 32 - hiking trails 27] Municipality of Hoyos selected the hiking trails function (Pict. 1) to valorize the local natural capital and increase and differentiate income sources. The test area (Pict. 2) pruning materials and mulching materials were used after clearing to test a mixture of aromatics growth based on seeding or seedling of local wild aromatic species, planted in stone terraces previously repaired (Pict. 3-4). The positive result of this test might lead to create areas where natural aromatic might be concentrated and used as income sources (bioservices), with the support of local companies to harvest and process plant material and sell the extracted soil mainly for cosmetic use. |
|||||
|
|
|||||